Pakistan Climate Change: Emerging trends & Issues

Pakistan Climate Change Trends
Pakistan Climate Change: Emerging trends & Issues! Pakistan possesses the continental type of climate, characterized by numerous variations of temperature levels. It happens both seasonally and regularly because of its location on the landmass north of the Tropic of Cancer.
Pakistan has recognized several environmental issues leading to climate change. Some of them are frequent variations in monsoons, decreased capacity of water reservoirs, and the Himalayan glaciers impacting the Indus river system have been the emerging problems in the country. Several natural hazards like frequent and severe earthquakes and flooding near the Indus river after heavy rains are the major causes of climate change concerns.
Climate Regions
Pakistan enjoys different varieties of environments depending upon geography and periods. The north and north-west high mountain ranges are considerably pleasant in summer months from April to September, while it is very cold in winter. Around the Indus valley, it is extremely hot in summer and the same level of cold in winter. There remains a temperate climate in the coastal strip in the South. However, the rainfall level is noted as low. It falls late in summer with an average range of 76 cm annually.
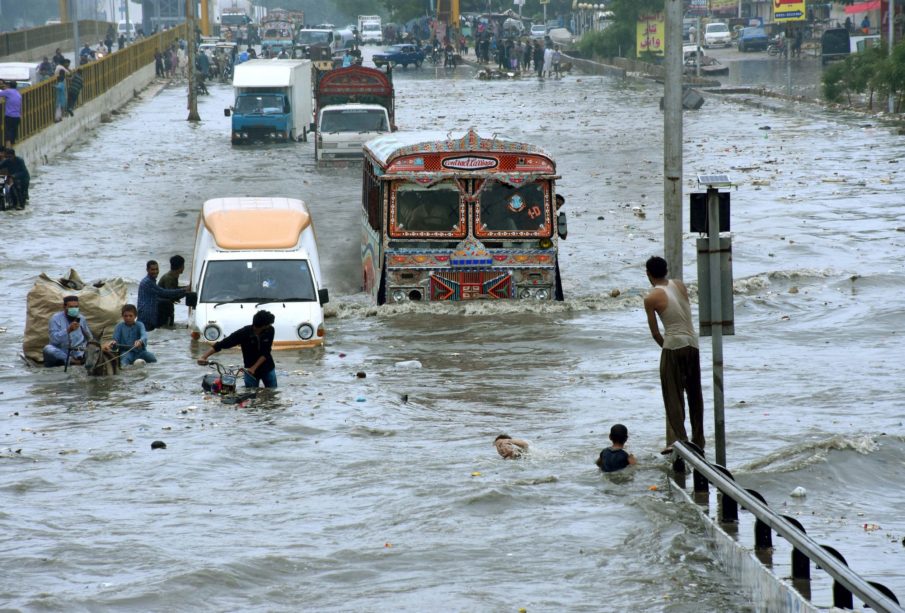
Torrential rainfall claims many lives and causes property and infrastructure damage. Other current climatic trends also impact different sectors such as transport, health, energy, agriculture, water, and especially coastal areas.
Overall, the climate in Pakistan has become volatile, and this trend is projected to continue in the future too.
Environmental Issues
The lion’s share of the population faces the scarcity of natural freshwater resources, water pollution from agricultural and industrial wastage, deforestation, desertification, and soil erosion.
Rainfall trend
Pakistan received lesser rainfall in January 2021 as compared to 2020. It was 59pc below the normal. Thus, the rainfall trend is going towards the 17th driest month in 60 years, symbolizing the possible impact of climate change. Likewise, the amount of rain in February also reinforced the declining trend. KP, Sindh, and Balochistan have noted a drastic decrease.
The real-time impacts are evident that the weather patterns have been becoming more pronounced as time passes.
Pakistan has been included in the list of the ten nations most affected by climate change.
Moreover, the country’s climate is causing uncertain results like devastating floods and droughts, glacier melts, and high temperatures.
Greenhouse Gas Contribution
Though there have been many climatic variations, Pakistan contributes little to global greenhouse gas emissions. It is less than 1% of the world’s total.
Its vulnerability to the effects of climate change is due to lower adaptability to technical and financial capacity. The displacement of populations and threat to food and water security are other causes that worsen the situation.
Future estimations for Pakistan’s climate
1. Pakistan’s estimated the projection of the temperature increase to be more than the global average.
2. The frequency of hot days and nights is projected to increase.
3. The temperature increase in southern parts would be lower than in the northern parts.
4. There seems a decreasing trend in the rainfall in the lower Indus Basin and an increasing trend in the Upper Indus Basin.
5. Extreme weather such as monsoons and cyclones tends to increase due to the rise in sea and atmospheric temperature.